What is Azure Cosmos DB?
Azure Cosmos DB is Microsoft’s latest multi-model database which can be distributed globally across any geographic region. Launched in 2017, Azure Cosmos DB is enhanced over and above its predecessor- Azure DocumentDB. Cosmos DB manages to excel and improvise over other players in the market via adherence to Service Level Agreements (SLAs) in terms of their performance including throughput, availability, and consistency. It is available to try Free of charge without any subscription or commitment.
-
Azure Cosmos DB Architecture
To understand the key functionalities of Azure, it is important to analyze its underlying architecture from a high level:
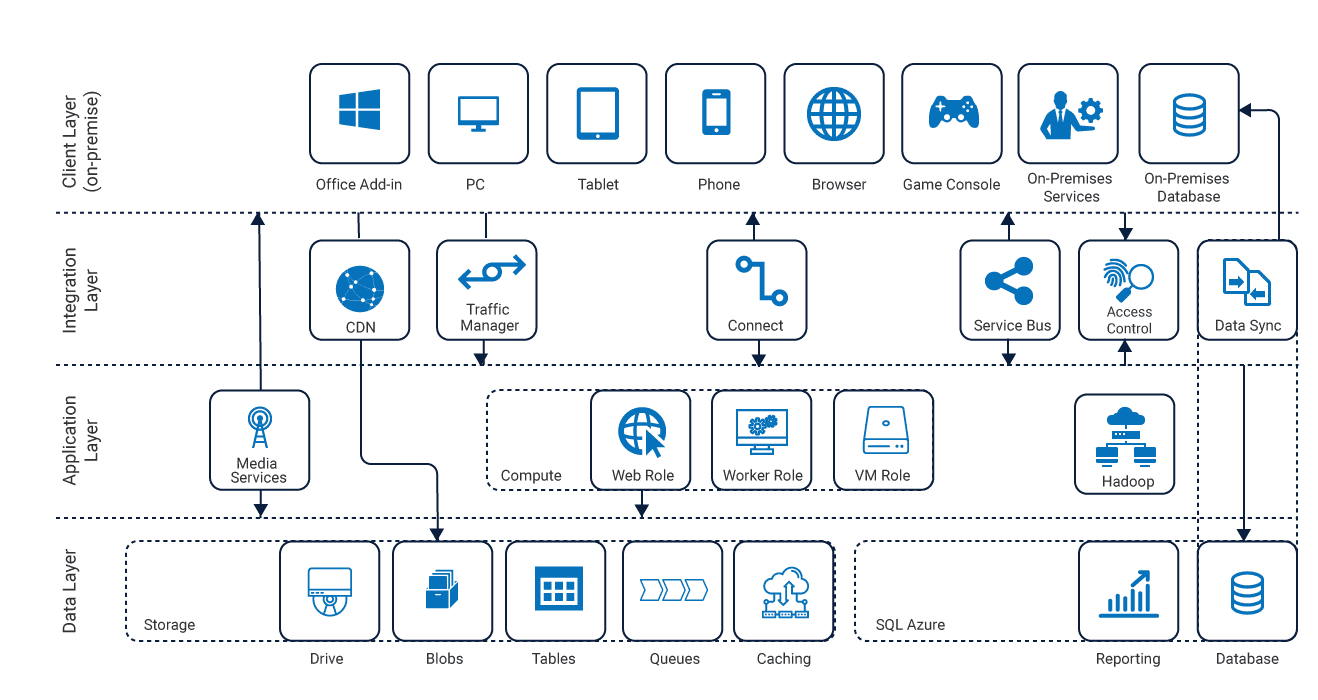
The figure above clearly indicates how Azure Cosmos DB functions in the data layer. Drilling down to the basics will yield more information on its Scalability, Resilience and Availability making it the front-runner for databases today.
Azure Cosmos DB vs. Architectural Styles
To understand the benefits of Azure holistically, it is imperative to look at how Azure is compatible with each of the following popular architectural styles:
The traditional N-tier architecture for enterprise applications manages dependencies by dividing them into layers performing logical functions. Every new layer sits below the previous layer in a horizontal fashion. N-tier is used for migrating existing applications using infrastructure as a service (IaaS) solutions, or applications that use a mix of IaaS and managed services. Azure Cosmos DB can be deployed seamlessly with N-Tier architecture when used as an IaaS.
For a PaaS solution, a Web-Queue-Worker architecture provides a web front end handling HTTP requests and a back-end worker performing long-running operations communicating with each other through an asynchronous message queue. With Azure’s use as PaaS, this style of architecture is also suitable and deployable.
For a more complex domain, Microservices architecture is ideal where API contracts are used for communicating between services. With the use of DevOps culture and Azure’s flexibility, Microservices contribute to one of the key factors for its popularity.
Last but not the least, Event-Driven Architectures using a publish-subscribe (pub-sub) model, are capable of handling applications ingesting and processing huge chunks of data with minimum latency, Azure Cosmos excels in here as well with its scalability. Internet of Things(IoT) is an ideal example
Apart from supporting the above conventional styles of architecture, Azure Cosmos DB also supports Big Data and Big Compute making it one of the most versatile solutions in the market today.
Design Principle, Quality Control and SLAs
Azure inculcates the following 10 design principles for its hosted applications:
- Self-healing
- Redundancy
- Minimal Coordination
- Design to scale out
- Partition control
- Design for operations
- Managed services
- State-of-the-art storage technology
- Design for evolution
- Relevant business needs
Azure Cosmos DB follows the 5 criteria for quality adherence with well-defined Service Level Agreements (SLAs):
- Scalability: The capability to handle increased load using both horizontal and vertical scaling
- Availability: The functional success of a system depends upon its availability with minimum downtime. Azure adheres religiously to well-defined SLAs to make sure these objectives are met.
- Resiliency: The capability to recover from failure and resume performance is built within Azure including services like Azure Storage, Azure Managed Disks and Virtual Machines or VMs.
- Management: Seamless operation of processes which keeps its system up and running is achieved using the DevOps model and implemented successfully by Azure.
- Security: Threat protection and intrusion detection processes in place to facilitate data safety using services like Azure Security Center.
In the following section, we are going to explore these attributes in further detail with respect to its Key Features.
Key Features:
Dynamic availability:
Data can be distributed globally to any number of Azure regions with just a click of a button, thereby allowing storage nearest to the customers reducing possible latency issues. This is achieved using Azure’s multi-homing APIs which identify the nearest data center to the user’s location. It allows flexibility to allocate multiple numbers of regions without any changes in configuration or availability of the stored data.
On-demand storage:
Scaling of storage In Azure Cosmos DB is transparent and automatic to make your data management easier. It supports the following 2 types of containers across all APIs:
Fixed Container: Fixed containers can store up to 10 GB with a maximum of 10,000 request units per second (RUPS). Fixed containers are created without specifying any partition key property in the data.
Unlimited container: Unlimited containers can automatically scale data beyond 10-GB through horizontal partitioning with auto-balancing of data based on the partition key specified. This allows storage of virtually unlimited amounts of data up to 100, 000 request units per second or more by getting in touch with their support team.
Partitioning capability:
Cosmos DB allows automatic partitioning capability using containers for storing data titled collections (for documents), graphs, or tables. These Containers or logical resources span physical partitions or servers. Cosmos DB determines the number of partitions across servers based upon the size of storage and throughput commissioned for the container. Each document is assigned a partition key and a row key for unique identification and prevents Azure Cosmos DB from distribution across various physical partitions.
The two types of possible partitions are:
Physical Partition: These partitions provide fixed SSD-Backed storage with variable compute resources namely CPU and Memory. Azure automatically scales the number of physical partitions based on workload and hence the identification of the right partition key is important.
Logical Partitions: Logical partition is a partition within a physical partition which stores all data with a pre-defined partition key value. As a result, multiple logical partitions can be stored in the same physical partition.
Let us look how partitions are achieved in Azure Cosmos DB.
Documents consist of a Partition Key and a Row Key, unique identifiers which form the backbone of the partitioning system. Partition Keys form the logical partition of the data which reside within a single physical partition managed by Azure Cosmos DB succinctly.
To achieve successful partitioning in Cosmos DB, the following are imperative:
- Provision a set of Azure Cosmos DB containers with RU/s (requests per second) throughput (denoted here as T).
- In the background, Azure Cosmos DB provisions its own physical partitions needed to serve these T requests per second. Now if T is higher than the maximum throughput per physical partition (denoted by t), then Azure Cosmos DB provisions N = T/t physical partitions.
- It allocates the key space of partition key hashes evenly across the N physical partitions. So, the number of logical partitions hosted by each physical partition is 1/N
- Now, if the storage limit for p is exceeded, Azure Cosmos DB splits p up into 2 new physical partitions- p1 and p2 by distributing almost half of its keys to the new physical partitions.
- If throughput value> t*N is commissioned, one or more of the physical partitions are split to accommodate it.
The following table denotes the partition key for the various API for Cosmos DB:

Note: Azure Cosmos DB hashes the partition key value and uses the hashed result to determine which physical partition to store the item in. Items with the same partition key values are in the same physical partition.
Creating Partition Key:
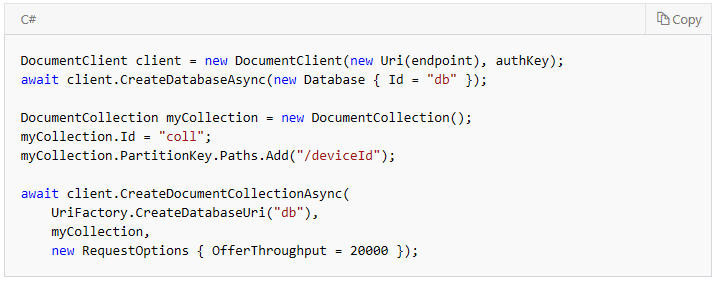
Create containers and scale them using Azure DB or Azure CLI specifying the throughput and the partition key. Here is how this can be achieved using various samples of API:
SQL API sample for creating a container:
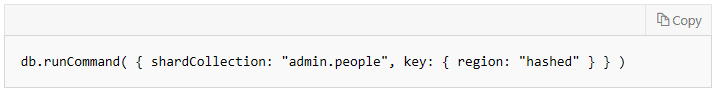
Mongo DB sample for creating a container in Mongo shell
The Result would be:
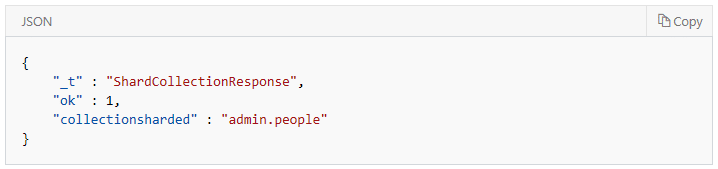
Table API sample to create a container using the CreateIfNotExists method
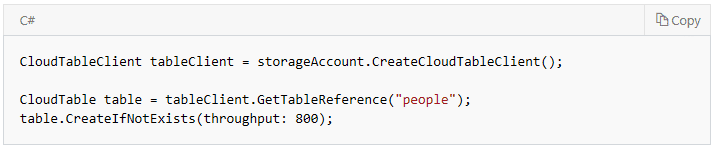
Partition Keys can also be created by concatenating and padding multiple property values into a single entity and are referred to as synthetic keys.
-
Multiple data model support:
Azure DB is built upon atom-record-sequence (ARS) which not only supports a wide range of data models but also caters to various formats like document, graph, key-value, table and column-family data for flexibility in storing data. The following APIS are supported along with their respective SDKs:
- SQL API
- Mongo DB API
- Cassandra API
- Gremlin API
- Table API
Transparent and automatic scaling of throughput
Azure Cosmos DB allows scaling storage size automatically to cater to various requirements. It is important to select a good partition key while creating your container. A few examples of a good partition key in a couple of scenarios are as below:
For a user profile backend, the user ID is an ideal choice.
For any Internet of Things-related data, either device state or a device ID is a good choice for a partition key.
Note: Partition keys with high volumes of data should be avoided to make sure all data for a single partition key should be stored within the same physical partition
Impressive SLAs with minimum downtime
Azure Cosmos DB ensures 99.99% availability for all single-region with 99.999% read availability on multi-region database accounts- a parameter unmatched by any other service provider in the market.
Cost-effective and competitive pricing
Cosmos DB comes with a money-back guarantee with strict adherence to Service Level Agreements (SLAs) for availability, latency, throughput, and consistency for data. The following table is a perfect example:
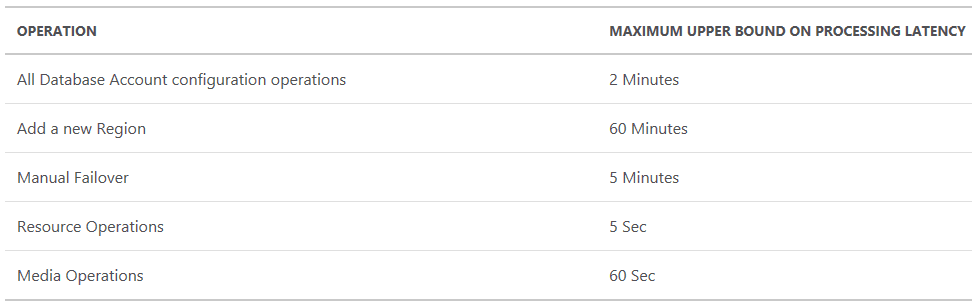
Super-fast query processing
The database engine for Azure processes queries at blazing fast speeds by indexing the data and iterating the schema associated with the application making it hassle-free and convenient.
Java-script Engine
Cosmos DB runs on an embedded java-script engine which allows stored procedures, triggers, and user-defined functions to be executed seamlessly without any hindrance making it the most comprehensive database in the world today.
Advantages of Azure Cosmos
The key features of Azure pave the path for it to be the most sought after database in the world today. In a nutshell here are the features that make it stand out from other DBMSs and RDBMSs:
- Provides global distribution in 30+ regions in the world
- Provides independent scaling of storage and throughput
- Provides 99% of reads in <10 ms and writes in <15 ms
- Always-on and offers contingency plans in place for any unforeseen downtime
- Multi-model architecture with new features added every month
- Groundbreaking SLAs unmatched in the market today
Azure Cosmos DB Emulator
As mentioned earlier, Azure Cosmos DB is free to try. It provides an emulator service which allows developing and testing your applications using a local environment without any subscription. This emulator can be used with all the APIs including SQL, Cassandra, Gremlin, MongoDB, and Table.
System requirements for Emulator:
Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2016, Windows 10
2-GB RAM
10-GB available hard disk space
Windows Installation
To install the Azure Cosmos DB Emulator, follow the steps below:
- Download and install the Azure Cosmos DB Emulator from https://aka.ms/cosmosdb-emulator.
- Select Start or press Windows. Select Azure Cosmos DB Emulator from the list of applications.
The Azure Cosmos DB Emulator runs on the local machine (“localhost”) using port 8081 and is installed to C:Program FilesAzure Cosmos DB Emulator by default.
Once the emulator is launched, the Data Explorer is launched to check for any available updates. Download the updates if available.
Development with Emulator
You can use the Azure Cosmos DB SDK or the Azure Cosmos DB Rest API to start your interaction. The built-in data explorer allows you to create collections for SQL and MongoDB APIs with least effort.
The Command Line (CLI) syntax to start the emulator is as follows:
CosmosDB.Emulator.exe [/Shutdown] [/DataPath] [/Port] [/MongoPort] [/DirectPorts] [/Key] [/EnableRateLimiting] [/DisableRateLimiting] [/NoUI] [/NoExplorer] [/?]
Azure Cosmos DB Database Security
Security plays a vital role in deploying any new applications and with Azure Cosmos DB regular updates are provided to ensure adherence. Encryption at rest is available as the latest addition to the security umbrella making your data safe and secure.
The following diagram borrowed from Microsoft’s whitepaper lays down clearly how a PaaS cloud database provider like Azure Cosmos DB reduces risk and vulnerability against others:
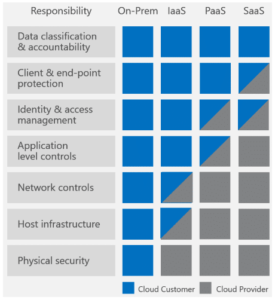
Security features for Azure Cosmos DB
Network Security
Azure Cosmos DB uses IP firewall as the first layer of protection to secure its database. Preventive measures are in place to make sure that these accounts are only accessible by authorized users via specific IP addresses, IP range, and their unique combinations for added security.
Authorization
Using hash-based message authentication code (HMAC) for authorization, Azure has secured the authentication process manifold ahead of its competitors. Requests are hashed using the secret account key, and the subsequent base-64 encoded hash is sent to Azure Cosmos DB for verification. After successful validation, the authorization is granted.
Users and Permissions
Azure Cosmos DB allows resource-based access to its databases using Resource Tokens. These tokens are used to validate the user’s access to numerous resources including container, documents, attachments, stored procedures, triggers, and UDFs and also allow assigning Read, Write and Edit permissions depending on their hierarchy.
RBAC integration
Azure allows access to its database account using Access control (IAM) in the Azure portal using role-based permissions depending on the levels of access required by its users. This integrates better control and transparency on the entire access control model with specific roles assigned to designated users.
Global replication
Azure Cosmos DB allows your data to be replicated to any one of their worldwide data centers with the click of a button. This also ensures data protection against regional failures.
Automated online backup
Azure Cosmos DB databases are backed up regularly online which if required can be used to recover data even after 30 days of accidental deletion.
Attack and Threat monitoring
Data stored within a Cosmos DB database uses adult logging and activity logs for any abnormal activities in the account. In the event of a report of data threat, the Support team initiates a 5-step incident response process to aim towards speedy resolution after a thorough investigation of the issue.
HTTPS/SSL/TLS encryption
Azure interactions are SSL/TLS 1.2 compliant including all their data centers and repositories.
Azure Cosmos DB: Use Cases
Azure Cosmos DB with its automatic scaling, high performance and schema-free data queries at lighting fast speeds is ideal for today’s cutting-edge applications. This has made it the choice for Gaming and IOT related devices like smart appliances. Now, let us have a look at a couple of use cases to understand how Azure has shaken things up in the database market.
Use Case 1: IOT and Azure
Internet of things is the reality of today shaping future growth through revolutionary ways of processing and storing data. Smart appliances use device sensors located at different corners of the globe to absorb data and process them via Analytics for real-time insights. Azure offers services like Azure Event Hubs, Azure Stream Analytics, Azure Notification Hub, Azure Machine Learning, Azure HDInsight, and PowerBI to name a few for putting this data to successful use. The following diagram explains this in detail:
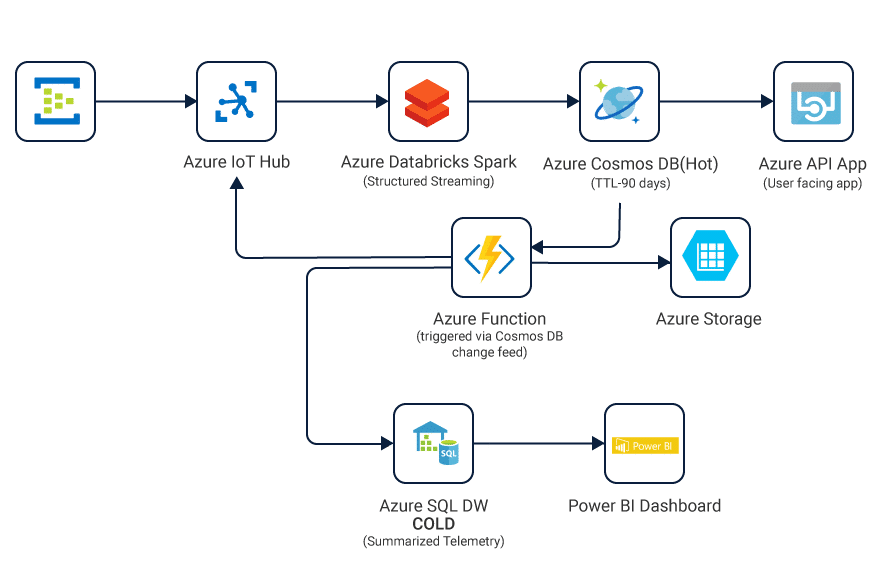
Azure Event Hubs ingest huge chunks of data and send them over to Azure Stream Analytics to process in real time. Change feed can be used to record any changes to existing data or inclusion of new data in Azure. Not only does it store the data sequentially in containers but also allows them to be refined and processed using HDInsight. The refined data is then loaded back to the Azure Cosmos DB for reporting and further analysis.
Use Case 2: Mobile Applications
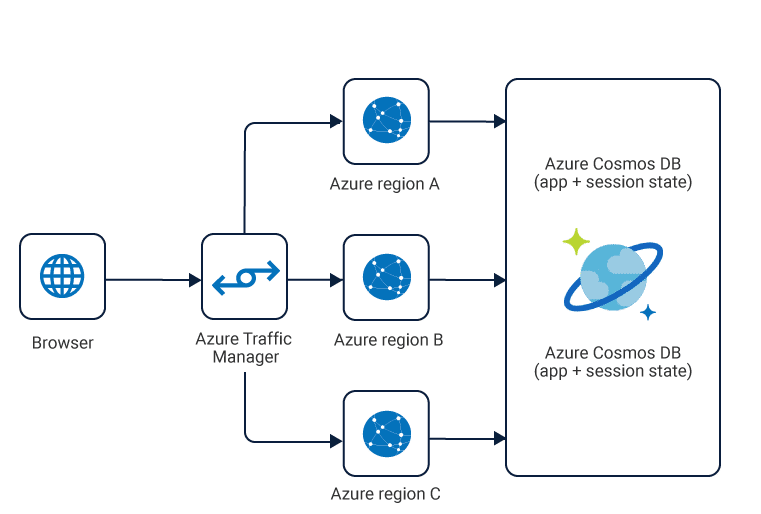
In today’s world of Social Media, most user-generated content (UGC) for mobile or web apps are stored in Azure Cosmos. Examples include chat sessions, tweets, blog posts, ratings, and comments.
These applications run globally and exhibit unpredictable usage patterns. Flexibility in scaling the data store is of utmost importance to keep up with their ever-increasing demand. Cosmos DB allows scaling out by adding additional data partitions under an account or by adding new accounts for newer regions.
Azure Cosmos DB: Where it stands today
Azure Cosmos DB has received tremendous impetus and popularity due to the one size fits all approach of Microsoft Corporation and is currently one of the more popular databases leaving behind its competitors like DynamoDB from Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Google BigQuery. The big question is will cloud-based databases like Azure take over traditional RDBMSs like Oracle, Microsoft SQL, and MySQL? We have to wait and watch. But the game has already started to change. According to Gartner Analyst Thomas Bittman, public clouds have shown a growth rate of 20X as compared to a 3X growth for private datacenters last year. The next few years will testify the winner, but Azure Cosmos DB definitely has its game on for now!
