What is Cloud Computing?
“Cloud is about how you do computing, not where you do computing,” goes a popular refrain in the domain of modern computing.
Definition
Cloud computing is the on-demand availability of computer system resources, especially database storage and computing power, without direct active management by the user. It is done through a cloud services platform via the Internet with pay-as-you-go pricing.
The essence of this statement seeks to debunk certain misconceptions that have risen in the popular imagination. Some of the popular myths related to the cloud include:
- Cloud computing represents a brand-new revolution
- All remote computing equals cloud computing
- Everything will be in the cloud
- The cloud eliminates private networks
- Every vendor will operate a different cloud, etc.
According to Amazon Web Services, “cloud computing is the on-demand delivery of computing power, database storage, applications, and other IT resources through a cloud services platform via the Internet with pay-as-you-go pricing.”
This definition represents the most concise narrative that describes this modern digital framework. As of date, three types of cloud computing service models pervade the cloud paradigm. These include Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). Customers of cloud computing services must select the correct configuration that best serves their requirements and helps them “strike the right balance of control and the avoidance of undifferentiated heavy lifting.”

Benefits of cloud-based computing
- Zero capital expense
Users can control their capital expenditure better when they opt for cloud computing services. This emerges from the fact such services allow users to pay only for the compute resources they consume in the course of doing business. The pay-as-you-go model liberates users from the specter of massive upfront capital expenditure on information technology hardware and software.
- Massive economies of scale
A large number of customers use significant volumes of cloud services in the present day. This generates massive economies of scale that translate into significantly lower costs for each customer of cloud services. These economies of scale also translate into real-world gains when start-up operators deploy cloud services on shoestring budgets.
- Scale infrastructure capacity rapidly
The providers of cloud computing services can respond in an instant to customer requirements for fluctuating computing capability. This ability saves customers from the considerable expenses associated with idle computing resources or dealing with sudden spikes in demand for raw computing power. Such a constant convenience allows cloud customers to focus on providing customers with superior user experience.
- Faster agility
Cloud computing elevates the power of a mouse click to a different level of performance. Customers of such services can summon immense compute power at the click of a mouse button. This lowers latency and boosts the ability of an organization to respond to multiple stimuli in its internal or external environments. For instance, developers working on special projects can access high levels of raw computing power in a matter of minutes, bypassing the bureaucracy of organizational red tape.

Or a simple version………
The benefits of Cloud-based computing include – Faster agility, rapid development, document control, backup and recovery, environment-friendly, infinite storage, cost proficient, streamline workflow, software integration, etc.
The future of Cloud
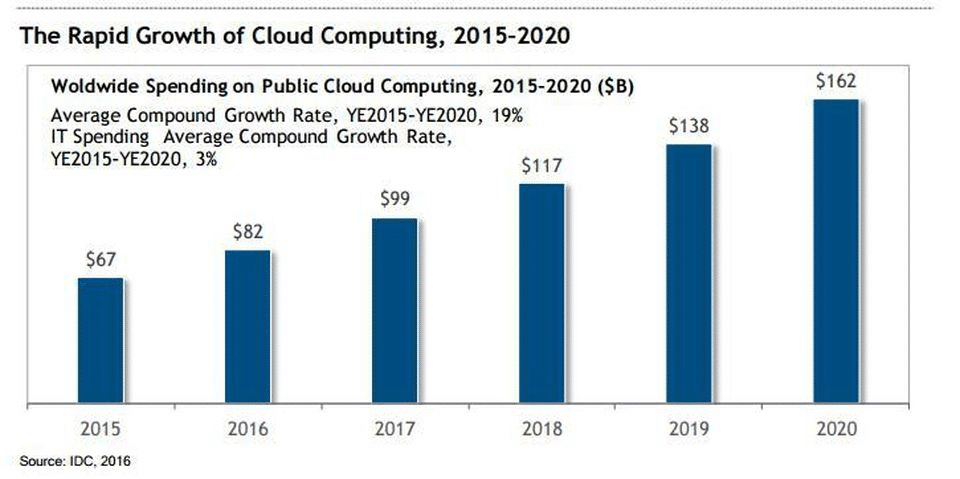
Rapid growth of cloud computing is predicted in the coming years. Leading cloud technologies are gaining an incremental share of enterprise IT budgets worldwide. Almost 59% of year-over-year growth in the spending on public cloud is predicted in recent times.
In a recent press note, IDC notes cloud platform technologies or leading cloud technologies are gaining an incremental share of enterprise IT budgets worldwide. Conversely, business operators are working to reduce spending on legacy, in-house information technology infrastructure, and resources. This duality has emerged as a defining theme in some of the commercial aspects of modern information technologies. IDC goes on to state that quarterly spending on public cloud IT infrastructure attained a valuation of $10.9 billion as of the second quarter of 2018. This represents almost 59% growth year-over-year in recent times.
Cloud Computing Concerns
Meanwhile, some concerns have emerged in terms of users’ ability to manage the proliferation of multiple cloud services and resources. “End users’ ability to utilize multi-cloud resources is an essential driver of further proliferation for both public and private cloud environments,” according to Natalya Yezhkova, a research director at IDC. This concern echoes in certain quarters that acknowledge cloud platforms “require expertise beyond what line of business managers possess, such as sales engineers, software trainers and application developers or testers who are utilizing cloud platforms but have little expertise outside their domain.” Consequently, they seek help and assistance from internal IT resources, thereby impacting the ability of said resources to respond to every individual request for assistance.
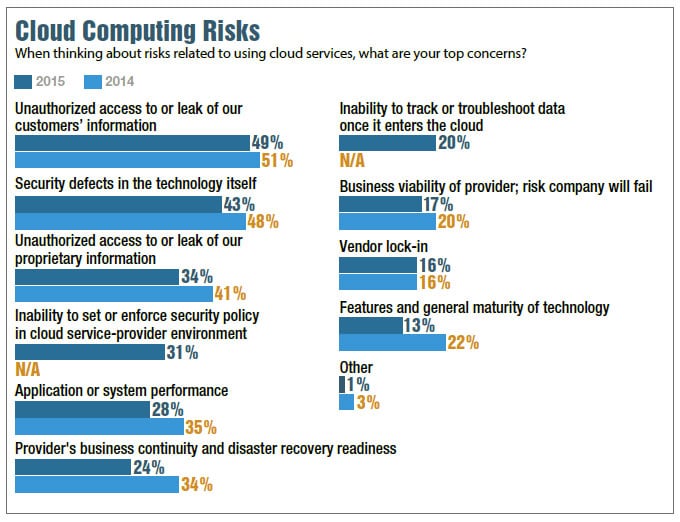
In a nutshell, unauthorized access to or leak of information, security defects, inability to set or enforce security policy, inability to track or troubleshoot data once it enters the cloud, application or system performance, vendor lock-in, etc.
A Cloud in Every Region
IDC research indicates a deep embrace between enterprises and modern cloud technologies, cutting across multiple geographies. As of the second quarter of 2018, every region on the planet witnessed double-digit growth in revenue generated by enterprise cloud services. The Asia-Pacific region, for instance, led with an estimated 79% growth year-on-year. In the same calendar quarter, cloud revenues in China grew at roughly 96%, while Latin America, the United States, and Japan grew at 47%, 45%, and 35%, respectively.
Major Cloud Providers Market Share: Jingle All the Way!
- Consequent to business confidence soaring in the cloud’s ability to deliver consistently, cloud service providers are working to craft deeper, strategic deals with their customers. Google CEO Sundar Pichai has gone on record to state, “We believe that Google Cloud platform, based on publicly reported data for the 12 months ending December 2017, is the fastest growing major public cloud provider in the world. Some deals worth over $1 million across all cloud products more than tripled from 2016 to 2017.” This statement underlined the fact that Google Cloud Platform has achieved the 1 billion USD per quarter milestone in recent times.
- Another cloud major, Amazon Web Services, went further and registered nearly 49% higher growth in the second quarter of 2018. The operator beat analyst expectations to generate 6.11 billion USD in revenues in that quarter. Market observers noted that Amazon’s cloud services, which debuted in 2006, has achieved impressive growth, at times touching 255% expansion in 12-month cycles. Consequent to these numbers, market analysts predict Amazon Web Services may double its revenues to an estimated 42 billion USD by 2020. Their optimism is borne aloft by the firm’s new product offerings and the visible momentum in cloud services uptake.
- Meanwhile, Microsoft’s Azure cloud services saw revenues from enterprise cloud services jump 58% to 6 billion USD in the first quarter of 2018. This was an outcome of “the rapid, sweeping and worldwide move by businesses across all industries into digital-first strategies that are allowing them to understand customers and opportunities more clearly, make better decisions more quickly, reduce costs while boosting quality, and embrace AI and data as indispensable elements within their operations.”
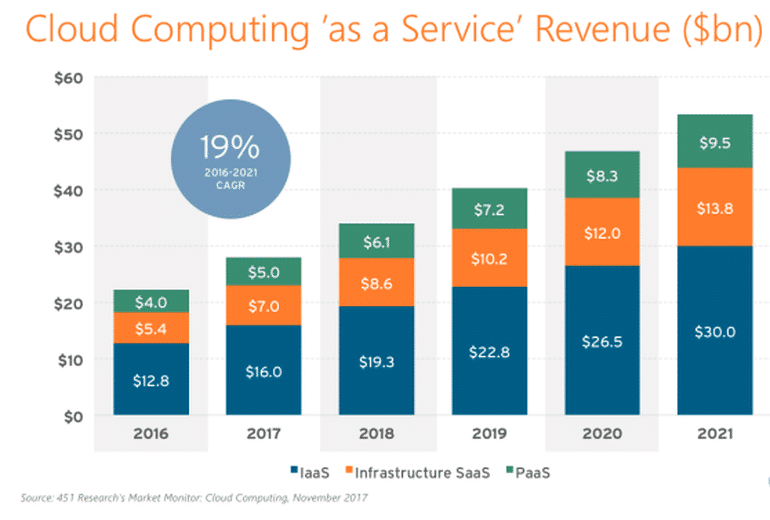
The Bottomline
As of March 2019, analyst firm Gartner asserts the cloud has “outgrown its classification as an emerging technology.” The firm remains upbeat about players across a wide spectrum of industries embracing the cloud paradigm at multiple levels. It estimates that cloud computing infrastructure and applications will corner the lion’s share of the total enterprise IT spend of roughly 3.77 trillion USD in 2019 alone. Further, Gartner states that the need for digital transformation will likely remain the key driver of growth for cloud computing services, adding that intelligent technologies (such as the Internet of things, machine learning, and artificial intelligence) will combine with cloud computing to “catapult companies into a new dimension of competitiveness.”
Further to the above, a specific set of technologies are emerging as important abstractions of modern cloud computing services. According to Gartner, blockchain, digital experience, server-less, artificial intelligence, and machine learning represent the dominant faction of cloud platform services and enterprise applications. This is in line with earlier predictions from industry observers that averred, “PaaS offerings will mature and expand the depth and breadth of their features. For example, as part of the expansion of the scope of their ecosystem services, PaaS offerings will increasingly provide not only business-level services but also application-level ecosystem services.” This implies, according to Gartner, that platform as a service (PaaS) service offerings may attain 20 billion USD in market revenue by the end of 2019.
General FAQ
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is the on-demand availability of computer system resources, especially database storage and computing power, without direct active management by the user. It is done through a cloud services platform via the Internet with pay-as-you-go pricing.
What are the benefits of Cloud-based Computing?
The benefits of Cloud-based computing include – Faster agility, rapid development, document control, backup and recovery, environment-friendly, infinite storage, cost proficient, streamline workflow, software integration, etc.
What are the problems with Cloud Computing?
Unauthorized access to or leak of information, security defects, inability to set or enforce security policy, inability to track or troubleshoot data once it enters the cloud, application or system performance, vendor lock-in, etc.
What is the future of Cloud?
Rapid growth of cloud computing is predicted in the coming years. Leading cloud technologies are gaining an incremental share of enterprise IT budgets worldwide. Almost 59% of year-over-year growth in the spending on public cloud is predicted in recent times.